INMARSAT Ltd. is a private satellite provider based in London, UK (http://www.inmarsat.com). It evolved from an inter-governmental organization to its current private status in the late 1990s. It operates a number of geostationary satellites covering the entire surface of the earth (except the polar regions) using global beams, and spot beams for the more traffic intensive regions.
The positions (orbital slots) of the two latest generations of INMARSAT satellites are listed in the table below.
|
Coverage Area |
Satellite Designation |
Orbital Position |
Former Country Code |
|
Atlantic Ocean Region West (AOR-W) |
3F4 |
54° W |
+874 |
|
Atlantic Ocean Region East (AOR-E) |
3F2 |
15° W |
+871 |
|
Indian Ocean Region (IOR) |
3F1 |
64° E |
+873 |
|
Pacific Ocean Region (POR) |
3F3 |
178° E |
+872 |
|
Asia, Pacific |
I-4 Asia-Pacific (4F1) |
143° E |
|
|
Europe, Middle East, Africa |
I-4 EMEA (4F2) |
25° E |
|
|
Americas |
I-4 Americas (4F3) |
98° W |
|
INMARSAT now uses +870 as a single country code for all regions (SNAC).
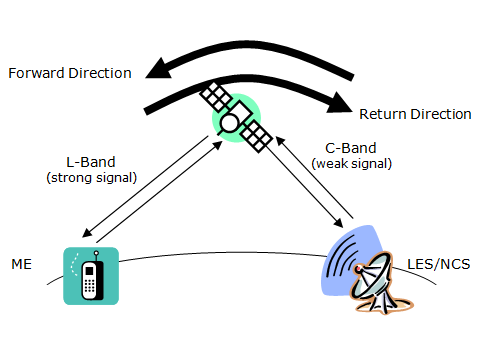
Each region has a system architecture as depicted below.

A region is controlled by a Network Control Station, NCS. Its functions are operation of the control channels and allocation of traffic channels and channel resources. Each region may encompass a number of Land Earth Stations, LES. Their functions are interfacing to terrestrial networks (PSTN, data networks, Internet), session control. The user terminals called a Mobile Earth Stations, MES, communicate with the NCS and LES. The NCS communicate with all LES within its control area. The LES and NCS continuously broadcast system information.
Note: The information in the following paragraphs applies to the land mobile and maritime systems offered by Inmarsat. The aeronautical services differ in channel naming, usage and system setup.