The techniques used to make the data more robust include framing, scrambling, error detection and correction and compression,and line conditioning using probing and training signals, which are used to adjust equalizers and echo cancellers at the far end to the actual phase, frequency and amplitude characteristics of the line.
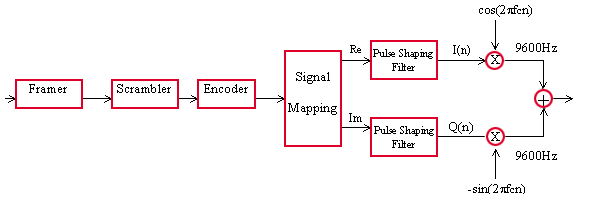
A schematic of the transmission section of a typical modem using phase modulation is shown below. Incoming data is framed as HDLC frames, scrambled to facilitate bit synchronization, and then encoded. The encoded signal is then mapped to the phase changes (and for QAM also to amplitude changes) and used to modulate a quadrature carrier.

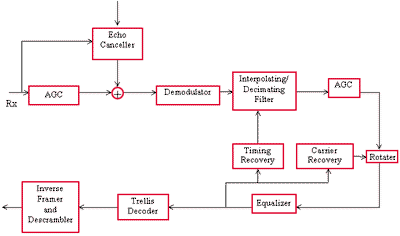
The receiving section will attempt to cancel out any echo, then demodulate the incoming signal, recover carrier and bit synchronism then finally de-frame and de-scramble the bit stream. The equalizer will attempt to invert line characteristics, and if Trellis coding has been used a Trellis decoder is inserted.